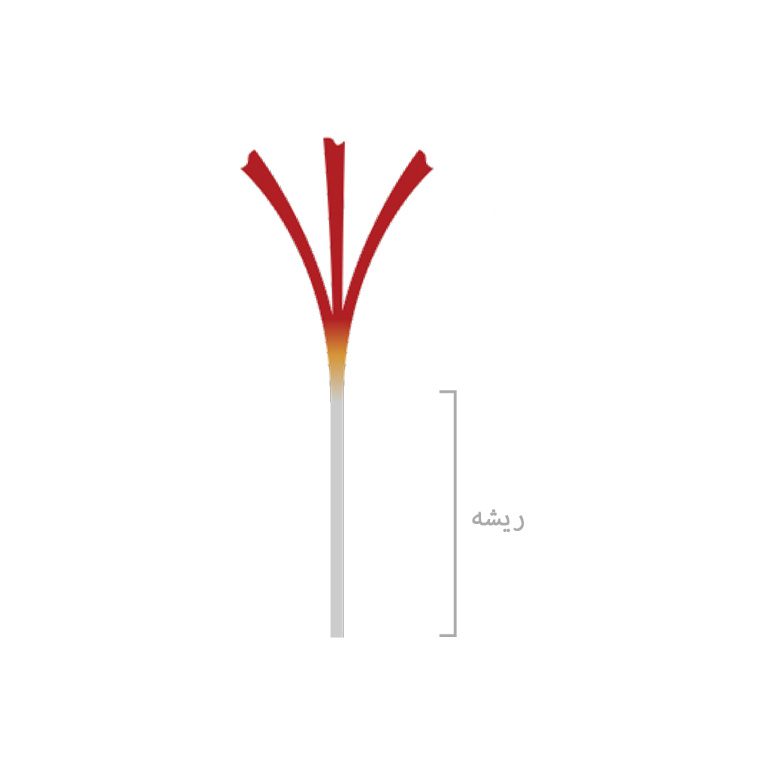
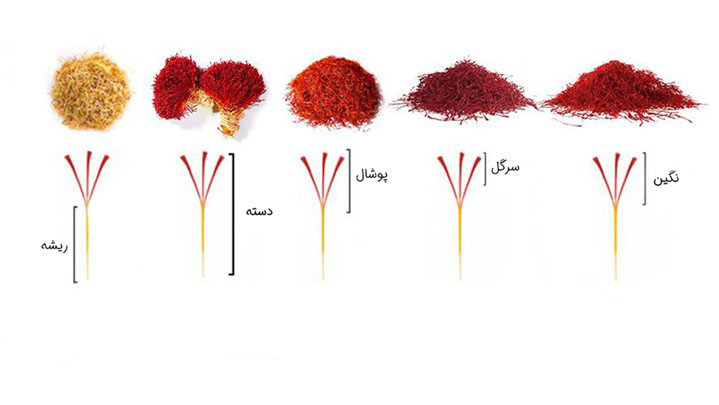
The saffron root, also known as saffron’s base or “khameh,” is the bottom part of the saffron stigma. This white to yellowish part at the end of the stigma is essentially the underground portion of the saffron. The saffron flower has six purple petals and three yellow stamens. When the petals are removed, three red threads, connected to the white or base part, are visible. When the red stigmas are bundled together with the white base, it is referred to as “saffron bunch” or “saffron dasteh.” If the red stigmas are arranged separately, it is considered high-quality saffron.
Warning!
Some dealers may dye saffron roots and sell them as stigmas. This type of saffron has poor coloring power, lacks quality, and may be harmful to health.
Properties of saffron root
The saffron root, similar to the stigma, contains vitamins B1, B2, B6, and C, as well as minerals like iron, manganese, and calcium, although in smaller quantities. Unlike the stigma, the saffron root has less crocin, which is the main coloring agent in saffron, leading to lower coloring power. However, the saffron root still has other beneficial properties and can be used for treating mood disorders such as depression, enhancing vitality, eliminating bad breath, skin rejuvenation, boosting sexual health, and improving heart and liver function. Additionally, the saffron root can serve as a tonic for the stomach and bladder.

Uses of saffron root
Due to its therapeutic properties, saffron root can be used in situations where coloring is not a concern, and only the medicinal benefits are desired. It can also be economically beneficial as it is less expensive than premium saffron. The saffron root can be used in dishes where only the flavor and aroma of saffron are important, such as tahdig, sweets, soups, stews, syrups, and teas that contain other coloring ingredients. Besides its medicinal applications, saffron root is also used in various industries including pharmaceuticals, chocolate-making, and cosmetics.